 |
 |
Epidemiology and Genetics Research Program
Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences
February 13, 2004 |
EGRP BULLETIN
From the Office of
Edward Trapido, Sc.D., Associate Director
Epidemiology and Genetics Research Program
Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences
National Cancer Institute
This issue of NCI's Epidemiology and Genetics Research Program (EGRP)
Bulletin brings you news about:
- Epidemiologists Margaret Spitz and
Graham Colditz Join EGRP Part Time
- New Web Section Highlights EGRP Grantees'
Research
- NIH Funding and Grants Administration
Seminars Set for Miami (May), Seattle (June)
- EGRP Web Site Identifies Training
Opportunities in Cancer Epidemiology
- Cancer Education and Career Development Award
- Cancer Prevention, Control, Behavioral, and Population
Sciences Career Development Award
- NCI Transition Career Development Award
- RFA for Training for New Interdisciplinary Research
Workforce
- NIH Mentored Career Development Awards Policy
Change
- Stipend Increase for Kirschstein National Research
Service Award
- And more
- NCI Established Investigator Award
Offers Protected Research Time
- Nominations Invited for NIH
Director's Pioneer Award
- NCI Announces New Policy on Large R01s
- Guidelines Updated on Support
for Scientific Meetings
- Registration with Central
Contractor Web Site A Must for Government-paid Travel, Contracts
- EGRP-sponsored Program Announcements
- Cohort Studies in Cancer Epidemiology
- Occupational Health and Safety Research
- Small Grants Program for Cancer Epidemiology
- Molecular Epidemiology of Cancers Associated with
Acquired Immunodeficiency
- Small Businesses Grants (SBIR and STTR Programs)
- EGRP Invites Discussion of Cohort
and Case-control Consortia
- EGRP-supported Research Resources
- Geographic Information System for Breast Cancer
Studies on Long Island
- Breast/Ovarian and Colon Cancer Family Registries
- Cancer Genetics Network
- International Haplotype Mapping
Project Underway
- New NCI Publications
- U.S. Predicted Cancer Incidence, 1999: Maps by
County, State from Spatial Projection Models
- Socioeconomic Variations in U.S. Cancer Incidence,
Mortality, Stage, Treatment, and Survival, 1975-1999
- Missed Our Latest News Flashes? Subscribe?
- NCI Pilots Weekly Newsletter, Plans and Priorities
for FY 2005 Published
- Guidance on Weather-related Delays in Grant Application
Submissions
[to top of page]
EPIDEMIOLOGISTS SPITZ AND COLDITZ JOIN EGRP PART TIME
  Epidemiology
and Genetics Research Program (EGRP) is delighted to be joined by two
highly respected epidemiologists who are working part time in its offices
under the Intergovernmental Personnel Act (IPA). Margaret Spitz, M.D.,
M.P.H., The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston,
and Graham Colditz, M.D., Dr.P.H., of Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston,
are spending about one day a month in EGRP. They will help to integrate
epidemiology within the Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences
(DCCPS), facilitate translation of EGRP-funded research, review the current
portfolio to identify gaps and duplications, help organize a conference
of grantees, and assist in recruiting new epidemiologists. Epidemiology
and Genetics Research Program (EGRP) is delighted to be joined by two
highly respected epidemiologists who are working part time in its offices
under the Intergovernmental Personnel Act (IPA). Margaret Spitz, M.D.,
M.P.H., The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston,
and Graham Colditz, M.D., Dr.P.H., of Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston,
are spending about one day a month in EGRP. They will help to integrate
epidemiology within the Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences
(DCCPS), facilitate translation of EGRP-funded research, review the current
portfolio to identify gaps and duplications, help organize a conference
of grantees, and assist in recruiting new epidemiologists.
[to top of page]
NEW WEB SECTION HIGHLIGHTS EGRP GRANTEES' RESEARCH
We've begun a new section on our Web site with highlights of research
conducted and published by grantees supported through EGRP. Our investigators
are very productive, and we can't begin to do justice to all the research.
We welcome suggestions on additions. Access the Web section directly,
or through our Home page.
Contact Linda Anderson, e-mail: andersoL2@mail.nih.gov.
[to top of
page]
NIH FUNDING AND GRANTS ADMINISTRATION SEMINARS SET
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is offering two regional seminars
on research funding and grants administration this year. These seminars
are targeted toward researchers new to NIH, research administrators, post
docs, and trainees. Hands-on computer training in NIH electronic research
administration also is offered. The seminars will be held:
- May 6-7, Miami, Fla., hosted by the University of Miami and Florida
A&M University, College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences
(hands-on computer labs on May 5); and
- June 24-25, Seattle, Wash., hosted by the University of Washington
School of Medicine (hands-on computer labs on June 23).
NIH Guide,
NOT-OD-04-018
[to top
of page]
EGRP WEB SITE IDENTIFIES TRAINING OPPORTUNITIES IN CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY
EGRP has a new Web site with information about extramural and intramural
training opportunities for individuals who are interested in pursuing
careers in cancer epidemiology. Use this site as a gateway to become acquainted
with opportunities available at various stages of career development -
from the young investigator pursuing a doctoral degree to the established
investigator. Also use the site to access related resources, such as the
NCI publication "Everything
you wanted to know about the NCI Grants Process…but were afraid to
ask." Tell others about the Web site, which is accessible
directly, or through our Home
page.
Of particular interest may be the:
- Cancer Education and Career Development Award (R25T), which
was developed for our Division, supports institutional or multi-institutional
programs that will train multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary predoctoral
and postdoctoral fellows in highly interdisciplinary, team-oriented
research settings. This program requires sustained leadership, dedicated
faculty time, specialized curriculum development and implementation,
interdisciplinary research environments, and more than one mentor per
trainee to achieve career development research and education objectives.
Fact
Sheet
NIH Guide,
PAR-03-148
- Cancer Prevention, Control, Behavioral, and Population Sciences
Career Development Award (K07), also developed by our Division and
reissued this month, supports the career development of investigators
who have made a commitment to focus their research endeavors on cancer
prevention, control, behavioral, and the population sciences. Protected
time is provided through salary and research support for up to five
years to individuals with a health professional or science doctoral
degree who are 1) already proficient in general epidemiology, behavioral
sciences, or other relevant disciplines, and now want to make use of
these proficiencies in cancer-focused research careers in prevention,
control, population and/or the behavioral sciences, or 2) are already
trained in cancer epidemiology, etiology, prevention, control, and the
behavioral and population sciences but are not yet fully independent
investigators.
Fact
Sheet
NIH Guide, PAR-04-055
- NCI Transition Career Development Award (K22) facilitates the
transition of investigators from the mentored stage of career development
in academic cancer research to the independent stage. The award provides
protected time through salary and research support for up to three years
to postdoctoral individuals (who are not required to have a sponsoring
institution at the time of application) transitioning into their first
independent position, and investigators within the first two years of
their first independent cancer research position, to develop and initiate
their first independently supported cancer research programs. The award
targets clinicians pursuing basic science cancer research careers, careers
in patient-oriented cancer research, or careers in cancer prevention,
control, behavioral or population sciences; and doctoral degreed (e.g.,
Ph.D., D.Sc.) individuals pursuing research careers in cancer prevention,
control, behavioral or population sciences.
Fact
Sheet
NIH Guide, PAR-04-040
- Training for a New Interdisciplinary Research Workforce (T90)
is sponsored through a Request for Applications (RFA) and is to encourage
and enable development of an interdisciplinary workforce by ensuring
that undergraduate, predoctoral, and postdoctoral students receive the
didactic and research experiences necessary to lead and/or engage in
integrative and team approaches to solve complex biomedical and health
problems. The RFA is part of the new NIH Roadmap for Medical Research
in the 21st century.
Applications are due March 10.
NIH Guide, RFA-RM-04-015
NIH Roadmap
Initiative
- A Policy Change for NIH Mentored Career Development Awards
(K awards) now allows recipients to hold concurrent support from their
career award and a competing research grant when recognized as a Principal
Investigator or subproject Director. Mentored career award recipients
in the last two years of their support period will be permitted to reduce
the level of effort required for the career award and replace that effort
with an NIH research grant or subproject provided they remain in a mentored
situation. This policy permits candidates who are ready to apply for
and receive NIH research support to continue to benefit from the period
of protected time offered by the career development award.
NIH Guide, NOT-OD-04-007
- Stipends have been increased for Kirschstein National Research
Service Award (NRSA) recipients in Fiscal Year (FY) 2004. The budget
changes are only for Kirschstein-NRSA awards made with FY 2004 funds,
and affect the stipend levels for undergraduate, predoctoral, and postdoctoral
trainees and fellows.
NIH Guide, NOT-OD-04-023
Additional training opportunities are described on the new EGRP
Web site.
[to top of
page]
NCI ESTABLISHED INVESTIGATOR AWARD OFFERS PROTECTED RESEARCH TIME
The Established Investigator Award in Cancer Prevention, Control, Behavioral
and Population Research (K05) provides established investigators protected
time to devote to research and to act as mentors for new investigators
and junior faculty members. The target candidates are outstanding established
scientists who have demonstrated a sustained, high level of research productivity
and significant contributions to cancer prevention, control, behavioral
and/or population cancer research. They must demonstrate the need to develop
and enhance their own research and a commitment to serve as mentors to
new scientists. The award provides salary support for up to five years,
and it is renewable for one additional five-year period. NCI is especially
interested in training and retaining scientists who conduct high-quality
research in cancer prevention, control, behavioral, and population sciences.
This award is an important part of the NCI Strategic Training Plan to
relieve researchers from administrative and/or clinical responsibilities
in order to help them focus on mentoring and research.
Fact
Sheet
NIH Guide, PAR-03-149
[to top
of page]
NOMINATIONS INVITED FOR NIH DIRECTOR'S PIONEER AWARD
NIH will invite nominations for the new NIH Director's Pioneer Award
Program to stimulate high-risk, high-impact medical research. The program
is part of the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research. To inaugurate this program,
NIH will provide up to $500,000 per year for five years to a highly select
group of individuals who have the potential to make extraordinary contributions
to medical research. Nominations will be accepted from March 1, 2004,
through midnight EST April 1, 2004, through the program's Web site. Visit
the site now to learn more about the initiative.
[to top of page]
NCI ANNOUNCES NEW POLICY ON LARGE R01s
NCI is seeing a marked increase in the number of unsolicited R01 applications
submitted with direct cost requests in excess of $700,000. Unfortunately,
this increase is occurring at a time when the budget is no longer doubling.
To allow NCI to optimally manage its resources and to ensure that all
areas of the cancer research continuum are appropriately supported, a
new funding policy is being implemented in FY 2004.
A separate payline will be established at each round for unsolicited
R01 grants with direct costs in excess of $700,000 for any one year ("large
R01s"). Every effort will be made to maintain the large R01 payline
as close as possible to the general R01 payline. However, the large R01
payline will be determined at each round, taking into consideration scientific
scope, scientific merit, and budgetary constraints.
Large R01s submitted in response to RFAs or PARs, which are not reviewed
by NIH's Center for Scientific Review (CSR), are currently not percentiled
and are not affected by this policy. Non-percentiled R01s have been selected
for funding on a case-by-case basis for several years.
This policy does not supercede or in any way change the NIH policy on
the Acceptance for Review of Unsolicited Applications that Request $500,000
or More in Direct Costs (NOT-OD-02-004), which requires advanced approval
of applications requesting in excess of $500,000 direct cost in any year.
Formal advanced approval to submit an application in excess of $500,000
is still required. This policy relates to the method NCI will use to select
large R01s for funding after peer review has been completed.
Inquires about the notice may be directed to the NCI Referral Office,
Division of Extramural Activities, 6116 Executive Blvd., Room 8041, MSC
8329, Bethesda, MD 20892-8329, Rockville, MD 20852 (for express/courier
service); tel.: 301-496-3428; fax: 301-402-0275 ; e-mail: ncirefof@dea.nci.nih.gov.
NIH Guide, NOT-CA-04-004
NIH Guide, NOT-OD-02-004
[to top
of page]
NEW GUIDELINES SET ON SUPPORT FOR SCIENTIFIC MEETINGS
NIH has updated guidelines on support for conferences and scientific
meetings (R13 and U13). Of particular note are:
- A major revision from the previous PA is a requirement that applications
for conference grant support now present a letter from the appropriate
NIH Institute/Center staff documenting advance permission to submit
an application.
- There are three annual receipt dates for all applications for support
of scientific meetings (April 15, August 15, and December 15, annually);
decisions about awards normally will be made within six months of submission.
- New guidelines have been issued on inclusion of women, minorities,
and persons with disabilities in NIH-supported conference grants: It
is NIH policy that organizers of scientific meetings should make a concerted
effort to achieve appropriate representation of women, racial/ethnic
minorities, and persons with disabilities, and other individuals who
have been traditionally underrepresented in science, in all NIH sponsored
and/or supported scientific meetings. Plans to seek appropriate representation
should be specified during selection of organizing committees, speakers,
and other invited participants, such as session chairs and panel discussants.
In addition, efforts should be made to encourage attendance by women,
minorities, and persons with disabilities at all NIH sponsored and/or
supported scientific meetings as a means of increasing their participation
in the particular scientific field. The quality of the proposed plans
to seek appropriate representation will be an evaluation criterion
used during the scientific and technical merit review of requests
for funding to support scientific meetings. This policy applies to
all domestic or international scientific meetings sponsored by and/or
receiving support from the NIH. Reasonable efforts must be made as
well, to fulfill the goals of this policy for single seminars sponsored
by NIH laboratories or extramural programs. Outreach Notebook for
the NIH Guidelines on Inclusion of Women and Minorities as Subjects
in Clinical Research is available to help investigators understand
and comply with the NIH's inclusion policies. Access it through the
guideline's
Web page.
NIH Guide, NOT-OD-03-066
- A Web site has been established to centralize information about conference
and meeting support. The site has contact information for NCI and other
participating NIH Institutes, Centers, and Offices, and links to detailed
information on specific interests and funding parameters. Check
periodically for the most current information.
NIH Guide, PAR-03-176
[to
top of page]
REGISTRATION WITH CENTRAL CONTRACTOR WEB SITE A MUST FOR GOVERNMENT-PAID
TRAVEL, CONTRACTS
In order to receive federal government funding to attend meetings and
conferences (aside from grant support) or a contract, you must register
on the Central Contractor's Web site. We cannot file the registration
on your behalf and cannot process travel until the registration is completed.
This is a federal-wide rule. There are two steps: 1) Use the Web site
to apply for a Data Universal Numbering System (DUNS) Number, and 2) use
the DUNS number to complete the on-line registration form. (This form
is in addition the payment enrollment (Automated Clearing House (ACH))
form that you may have previously completed for NIH.
Access CCR
Web site (see "CCR News").
[to top of
page]
EGRP-SPONSORED PROGRAM ANNOUNCEMENTS
- Cohort Studies in Cancer Epidemiology (R01) - This Program
Announcement (PAR) announces special receipt dates for R01 grant applications
from investigators who intend to initiate, competitively supplement,
or competitively renew population-based epidemiologic or survivorship
cohort studies of human cancers. Investigators using a linked R01 approach
for funding of multi-center cohort studies must submit applications
under PAR-04-011 if the sum total of the funding requests from all research
sites is $500,000 or more in direct cost in any study year. Due dates
are:
Letters of intent: May 1, 2004; new applications: June
1;
Letters of intent: Jan. 2, 2005; new applications: Feb. 1, 2005;
Letters of intent: Sept.1, 2005; new applications: Oct. 1, 2005.
Application receipt dates for competing continuations, competitive
supplements, and revised applications due: July 1, 2004, March 1,
2005, and Nov. 1, 2005.
Direct inquiries about scientific issues to Sandra
Melnick, Dr.P.H., Chief, Analytic Epidemiology Research Branch (AERB),
EGRP; e-mail: melnicks@mail.nih.gov.
NIH Guide,
PAR-04-011
Addendum, NOT-CA-04-001
- Occupational Health and Safety Research (R01) - This PA encourages
development of knowledge that can be used in preventing occupational
diseases and injuries and to understand better their underlying pathophysiology.
Direct inquiries about scientific issues related to
cancer epidemiology proposals to Kumiko (Kumi) Iwamoto, M.D., Dr. P.H.,
AERB Program Director; e-mail: iwamotok@mail.nih.gov.
NIH Guide, PA-04-038
- Small Grants Program for Cancer Epidemiology (R03) - This PAR
invites applications relating to cancer epidemiology with a primary
focus on etiologic cancer research. These are short-term awards intended
to provide support for pilot projects, testing of new techniques, or
development of innovative projects that could provide a basis for more
extended research.
Direct inquiries about scientific issues related
to cancer epidemiology proposals to Ginny Hartmuller, Ph.D., R.D.,
AERB Program Director; e-mail: hartmulv@mail.nih.gov.
NIH Guide, PAR-03-010
- Molecular Epidemiology of Cancers Associated with Acquired Immunodeficiency
(R01) - This PA invites grant applications for interdisciplinary studies
to better understand the molecular epidemiology and role of cofactors
in the etiology and pathogenesis of preneoplastic conditions and cancers
occurring among persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus
(HIV), specifically those cancers associated with viruses such as human
papillomavirus (HPV), Epstein Barr virus (EBV), human herpesvirus-8/Kaposi
sarcoma associated herpesvirus (HHV8/KSHV), and hepatitis viruses B
and C. The initiative also includes malignancies arising within the
context of acquired immunosuppression from non-HIV sources, such as
organ transplants, and include the oncogenic virus HTLV.
Direct inquiries about scientific issues related to
cancer epidemiology proposals to Vaurice Starks, AERB Program Director;
e-mail: starksv@mail.nih.gov.
NIH Guide, PA-03-024
- Small Businesses Grants - Small businesses may obtain support
through the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and the Small
Business Technology Transfer Research (STTR) Programs. These programs
are designed to support innovative research that has the potential for
commercialization. The STTR Program calls for partnership between small
businesses and research institutions. Learn
more about the Programs, and view research topics of interest to EGRP.
Direct inquiries to Jay Choudhry, M.S., EGRP Program
Director; e-mail: choudhrj@mail.nih.gov.
[to top
of page]
EGRP INVITES DISCUSSION OF COHORT AND CASE-CONTROL CONSORTIA
NCI is interested in facilitating development of new consortia of cohort
and case-control studies in order to accelerate research on gene-gene
and gene-environment interactions in the etiology of cancer. The creation
of such consortia is part of the revolutionary shift to "big science"
- where studies of the future will be conducted on a much larger scale
by multidisciplinary teams of scientists who pool their resources or conduct
parallel analyses. To discuss potential consortia arrangements for study
of gene-gene and gene-environment interactions, investigators may contact
Edward Trapido, Sc.D., EGRP Associate Director; e-mail: trapidoe@mail.nih.gov.
Visit EGRP's Web site for information about some
consortia activities, and read about the Institute's plans for research
on genes and the environment in NCI's
Plan and Budget Proposal for Fiscal Year 2005: The Nation's Investment
in Cancer Research.
[to top
of page]
EGRP-SUPPORTED RESEARCH RESOURCES
EGRP invites researchers to take advantage of its research resources:
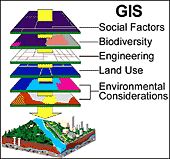 The
Geographic Information System for Breast Cancer Studies on Long Island
(LI GIS) provides a unique tool to study relationships between the environment
and breast cancer. The system is a rich resource of data and analytic
tools for environmental research. The system has more than 80 datasets,
including geographic, demographic, health, and environmental data, and
special built-in tools to facilitate its use. Although developed for
breast cancer research, the LI GIS also potentially can be used for
study of other types of cancer and other diseases and conditions. Funding
for research is not provided. The
Geographic Information System for Breast Cancer Studies on Long Island
(LI GIS) provides a unique tool to study relationships between the environment
and breast cancer. The system is a rich resource of data and analytic
tools for environmental research. The system has more than 80 datasets,
including geographic, demographic, health, and environmental data, and
special built-in tools to facilitate its use. Although developed for
breast cancer research, the LI GIS also potentially can be used for
study of other types of cancer and other diseases and conditions. Funding
for research is not provided.
Direct inquiries to Burdette Erickson, M.Sc., AERB
Program Director; e-mail: berickso@mail.nih.gov.
Visit the LI GIS Web site.
 The
Breast/Ovarian and Colon Cancer Family Registries (CFRs) are
international registries available to researchers who are planning to
conduct population- and clinic-based interdisciplinary research with
a main focus on the genetic and molecular epidemiology of breast/ovarian
and colon cancers. The CFRs have information and biospecimens contributed
by more than 19,000 families among whom there is a history of breast
and/or ovarian cancer or colon cancer. The spectrum of cancer risk is
represented. Of special interest are collaborations to identify and
characterize cancer susceptibility genes; define gene-gene and gene-environment
interactions in cancer etiology; and conduct cooperative research on
the translational, preventive, and behavioral aspects of such findings.
Researchers who are interested in accessing data and/or biospecimens
should explore collaborative arrangements with CFRs investigators and
prepare a brief application using the Access Policies and Procedures
Manual and the form located on the Informatics
Center Web site. Information about the CFRs also is available on
EGRP's Web site. Funding for research is not provided. The
Breast/Ovarian and Colon Cancer Family Registries (CFRs) are
international registries available to researchers who are planning to
conduct population- and clinic-based interdisciplinary research with
a main focus on the genetic and molecular epidemiology of breast/ovarian
and colon cancers. The CFRs have information and biospecimens contributed
by more than 19,000 families among whom there is a history of breast
and/or ovarian cancer or colon cancer. The spectrum of cancer risk is
represented. Of special interest are collaborations to identify and
characterize cancer susceptibility genes; define gene-gene and gene-environment
interactions in cancer etiology; and conduct cooperative research on
the translational, preventive, and behavioral aspects of such findings.
Researchers who are interested in accessing data and/or biospecimens
should explore collaborative arrangements with CFRs investigators and
prepare a brief application using the Access Policies and Procedures
Manual and the form located on the Informatics
Center Web site. Information about the CFRs also is available on
EGRP's Web site. Funding for research is not provided.
Direct inquiries to Daniela Seminara, Ph.D., M.P.H.,
Program Director, Clinical and Genetic Epidemiology Research Branch
(CGERB), EGRP, e-mail: seminard@mail.nih.gov.
- The Cancer Genetics Network (CGN) supports research on the
genetic basis of human cancer susceptibility, the integration of this
information into medical practice, and the psychosocial, legal, and
public health issues associated with human genetics. Its interests include
gene discovery and characterization, gene-environment interaction, and
translational and behavioral research.
The database has information on more than 18,700 individuals (14,850
families) with cancer and/or a family history of cancer. Data available
include demographic information, relevant medical history, and a four-generation
pedigree on each enrollee. The population enrolled makes research
possible on both common and uncommon tumors.
For approved studies, the CGN can offer a variety of services for
a fee(s), including:
- assembling information for and completing medical extraction forms
- obtaining pathology reports and tumor blocks for molecular testing
or to verify diagnosis
- collecting biospecimens with desired medical and demographic information
- shipping or storing biospecimens
- conducting telephone interviews with enrollees
- recruiting patients from high-risk clinics and tumor registries
- providing genetic counseling
- contacting enrollees' treating physicians prior to enrollment
- developing software, including computerized followup for the study
- using multiple software systems for breast cancer risk assessment.
Specialized expertise is available in certain areas, including biostatistics,
statistical genetics, epidemiology, genetic epidemiology, and behavioral
research. Also, CGN principal investigators welcome opportunities to
collaborate with research groups on important studies.
Researchers who are interested in accessing CGN data or including
registry enrollees in ongoing or proposed studies should prepare a 1-page
summary of their proposed research, specific aims, and explanation of
the role of CGN enrollees in the research. Priority is given to funded
investigators or to those who are planning to submit grant proposals
to NIH. Funding for research is not provided. For further information,
access the NCI CGN Web site.
Direct inquiries to Carol Kasten-Sportes, M.D., CGERB
Program Director, e-mail: kastenca@mail.nih.gov.
[to top of
page]
International Haplotype Mapping Project Underway
 The
International HapMap Consortium is creating a map of common patterns of
human genetic variations, or haplotypes, that will help researchers find
genes associated with cancer, other human diseases, and with response
to medicines. Some of the data are being released quickly and publicly
with no conditions, while some data can be accessed quickly by researchers
who agree not to restrict the use of the data by other researchers, and
to share the data only with those who have agreed to the same conditions.
The project is a public-private partnership of scientists and funding
agencies from Canada, China, Japan, Nigeria, the United Kingdom and the
United States. The U.S. component is led by the National Human Genome
Research Institute (NHGRI). Learn more about HapMap at these two Web sites:
http://www.hapmap.org/index.html
and http://www.nhgri.nih.gov/10001688. The
International HapMap Consortium is creating a map of common patterns of
human genetic variations, or haplotypes, that will help researchers find
genes associated with cancer, other human diseases, and with response
to medicines. Some of the data are being released quickly and publicly
with no conditions, while some data can be accessed quickly by researchers
who agree not to restrict the use of the data by other researchers, and
to share the data only with those who have agreed to the same conditions.
The project is a public-private partnership of scientists and funding
agencies from Canada, China, Japan, Nigeria, the United Kingdom and the
United States. The U.S. component is led by the National Human Genome
Research Institute (NHGRI). Learn more about HapMap at these two Web sites:
http://www.hapmap.org/index.html
and http://www.nhgri.nih.gov/10001688.
[to top of page]
NEW NCI PUBLICATIONS
 U.S.
Predicted Cancer Incidence, 1999: Complete Maps by County and State
from Spatial Projection Models. The results presented in this report
are computed by a spatial projection model that predicts the number
of cases in each county based on the sociodemographic and lifestyle
profile for that county. The purpose is to present, for the first time,
complete county and state maps and tables of rates and case counts for
1999 estimated by these new statistical models. From a national perspective,
the maps included in the report allow examination of the geographic
distribution of cancer incidence across the country and of the magnitude
of differences among states. Estimates of the numbers of new cancer
cases and rates expected in an area are useful for cancer surveillance,
cancer control, health resource planning, and quality control activities. U.S.
Predicted Cancer Incidence, 1999: Complete Maps by County and State
from Spatial Projection Models. The results presented in this report
are computed by a spatial projection model that predicts the number
of cases in each county based on the sociodemographic and lifestyle
profile for that county. The purpose is to present, for the first time,
complete county and state maps and tables of rates and case counts for
1999 estimated by these new statistical models. From a national perspective,
the maps included in the report allow examination of the geographic
distribution of cancer incidence across the country and of the magnitude
of differences among states. Estimates of the numbers of new cancer
cases and rates expected in an area are useful for cancer surveillance,
cancer control, health resource planning, and quality control activities.
Single print copies may be ordered from through NCI's
on-line Publications Locator, or the Cancer Information Service
(CIS): 1-800-422-6236. The
report also is available on-line.
 Area
Socioeconomic Variations in U.S. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Stage,
Treatment, and Survival, 1975-1999. This monograph analyzes area
socioeconomic differentials and trends in incidence, mortality, stage
of disease, treatment, and survival for all cancers combined and for
six major cancers (lung, colon/rectum, prostate, breast, uterine cervix,
and melanoma of the skin) by sex and race/ethnicity in the United States.
Order print
copies of this and other Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results
(SEER) Program monographs and reports. The
monograph also is available on-line. Area
Socioeconomic Variations in U.S. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Stage,
Treatment, and Survival, 1975-1999. This monograph analyzes area
socioeconomic differentials and trends in incidence, mortality, stage
of disease, treatment, and survival for all cancers combined and for
six major cancers (lung, colon/rectum, prostate, breast, uterine cervix,
and melanoma of the skin) by sex and race/ethnicity in the United States.
Order print
copies of this and other Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results
(SEER) Program monographs and reports. The
monograph also is available on-line.
[to top of page]
MISSED OUR LATEST NEWS FLASHES? SUBSCRIBE?
We had a problem with our ListServ recently, and you may have missed
our most recent News Flashes:
- Jan. 28: NCI Pilots Weekly Newsletter, Plans and Priorities for FY
2005 Published
- Feb. 2: Guidance on Weather-related Delays in Grant Application Submissions
They are posted in the Bulletins
section.
You are welcome to invite others to subscribe to EGRP's Bulletins and
News Flashes.
Contact: Linda Anderson, e-mail:
andersoL2@mail.nih.gov.
|